📌 Key Takeaways
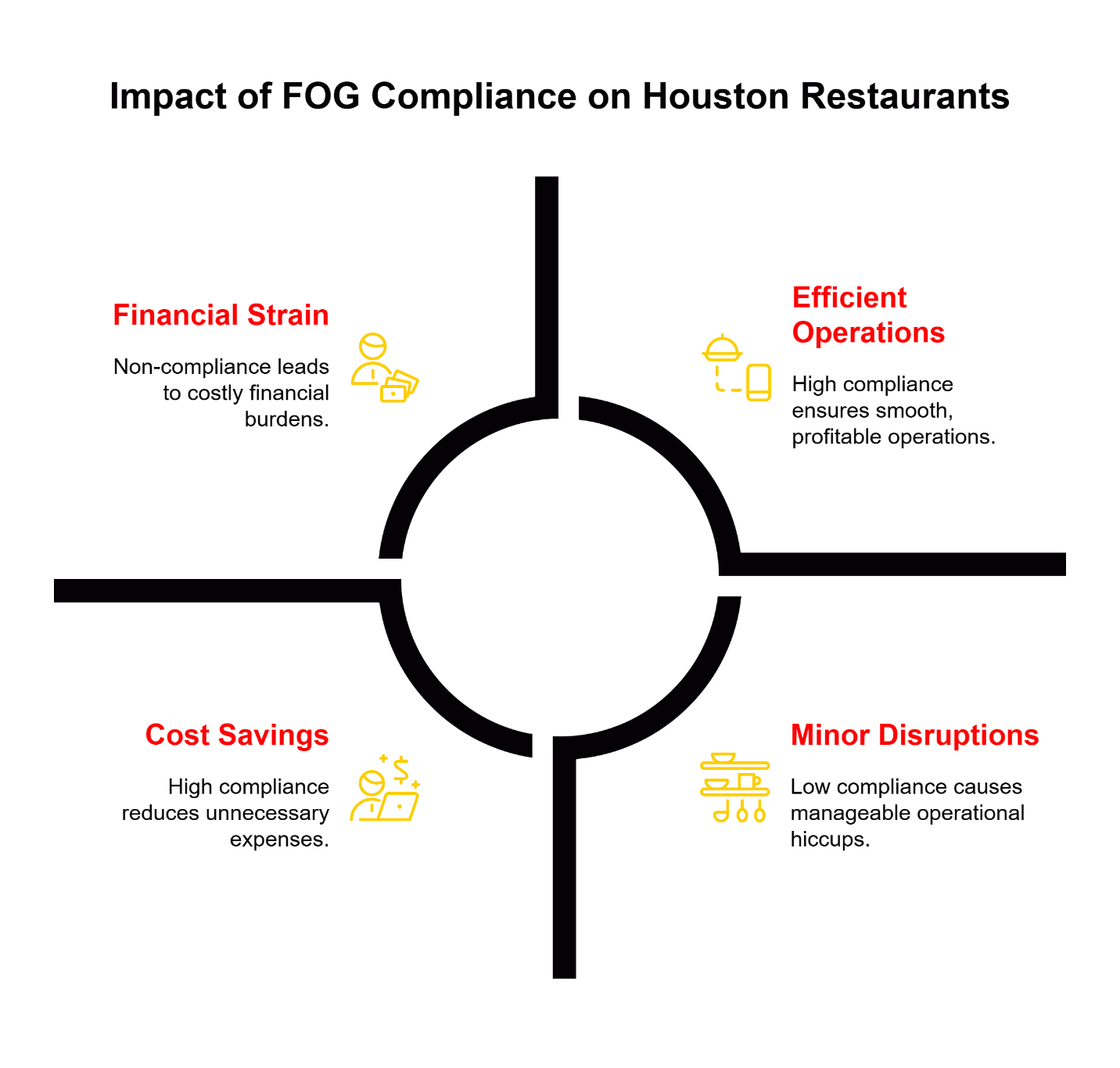
Hidden Costs Dwarf Compliance Fines: The city fine for grease trap non-compliance represents just a fraction of total failure costs—emergency shutdowns during peak hours can generate substantial lost revenue, premium after-hours service fees, staff overtime, and long-term reputation damage that extends far beyond the visible penalty.
Emergency Shutdowns Create Cascading Financial Impact: A single grease trap failure during dinner rush can halt kitchen operations for hours, requiring order refunds, emergency contractor fees at premium rates, health department re-inspections, and potential temporary closure orders that appear in permanent public records.
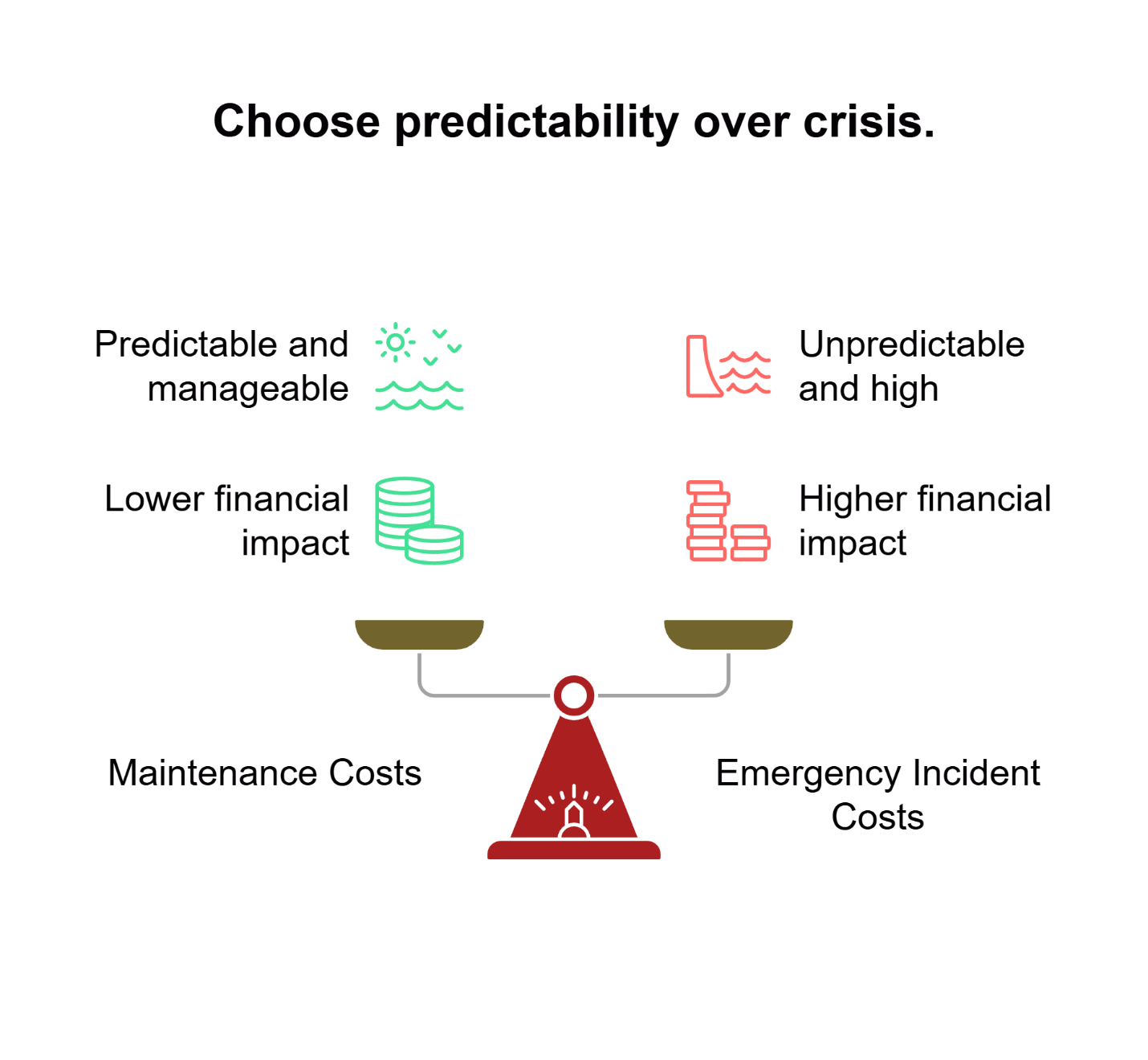
Prevention Costs Are Predictable, Failure Costs Are Not: Scheduled maintenance creates controllable operational expenses that protect against unpredictable emergency costs—transforming budget planning from reactive crisis management to strategic operational control that ownership teams can evaluate using standard business metrics.
Five Critical Cost Categories Emerge from Emergencies: Lost revenue during shutdown, emergency service premiums, staff disruption costs, regulatory compliance recovery, and long-term reputation impact create a comprehensive financial burden that extends well beyond the initial system failure.
Maintenance Framework Positions Managers as Strategic Leaders: Positioning preventative maintenance as risk mitigation rather than regulatory compliance demonstrates forward-thinking operational management—a skill set that becomes increasingly valuable for advancement to regional management responsibilities overseeing multiple locations.
This operational framework transforms grease trap maintenance from a cost center into a control center, providing the business case tools needed to secure budget approval while developing the systemic risk management skills essential for career advancement in restaurant operations.
When your boss questions the quarterly grease trap cleaning budget, they’re looking at the visible cost—the service fee. What they don’t see is the iceberg beneath the surface. The city fine for non-compliance might be manageable, but that’s just the tip. The real costs lurk below, waiting to sink your operational budget without warning.
For restaurant operations managers in Houston’s competitive food service landscape, this scenario plays out repeatedly. You know maintenance is necessary, but convincing cost-conscious ownership requires more than regulatory compliance arguments. It demands a complete picture of what happens when prevention fails.
The Tip of the Iceberg: Why City Fines Are Only the Beginning
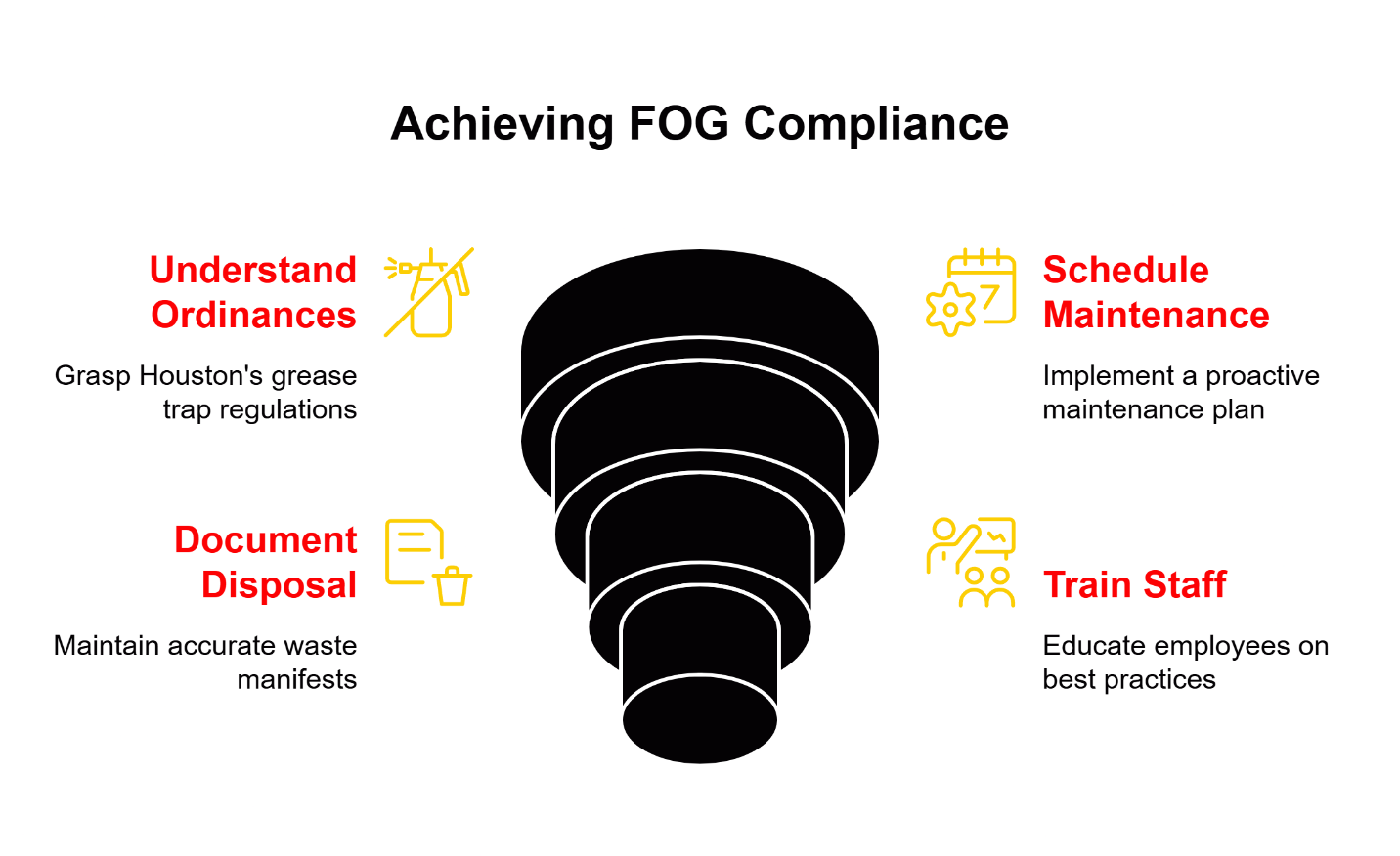
Houston requires regular cleaning of all commercial grease trap cleaning systems within city limits. The fine structure seems straightforward—a predictable penalty that many franchise owners factor into their risk calculations. But this thinking treats grease trap failure like a parking ticket when it’s actually more like a structural fire.
The compliance fine represents a small fraction of the total cost impact when a grease trap system fails catastrophically. Restaurant operations managers who’ve lived through a major backup understand this math intimately, but translating that experience into budget language requires breaking down the cascade of operational failures that follow a single clog.
Think of your grease trap system as the foundation of your kitchen’s waste management infrastructure. When that foundation cracks, everything built on top becomes unstable. The visible fine is just the first domino to fall.
The Domino Effect: How One Clog Shuts Down Your Entire Operation
Picture this scenario: It’s Friday evening during your dinner rush. Orders are flowing, staff is hitting their rhythm, and suddenly—complete drainage failure. Wastewater backs up into prep sinks, floor drains overflow, and your kitchen becomes a health hazard zone. What happens next isn’t just inconvenient; it’s financially devastating.
The Cost of Downtime: Calculating Lost Revenue Per Hour
A quick-service restaurant faces immediate revenue loss the moment kitchen operations halt. But the calculation extends beyond simple hourly revenue. Customer orders already in progress must be refunded or remade. Drive-through lines that stretch into neighboring businesses create reputation issues that persist long after the clog clears.
Grease trap emergency shutdowns can last several hours—time needed for emergency service calls, system cleaning, and health department re-inspection. During peak dining periods, this translates to substantial revenue loss before considering any additional complications.
The Ripple Effect: Staff Overtime, Emergency Repairs, and Damaged Reputation
Emergency repairs don’t follow normal business hours or standard pricing. Weekend emergency grease trap service calls typically cost significantly more than standard rates. Staff members sent home during the shutdown still require compensation, while others work overtime during the cleanup process.
The cleanup itself becomes a labor-intensive operation requiring specialized equipment and potentially hazardous waste disposal protocols. What would normally be a routine maintenance visit transforms into an all-hands emergency response involving multiple contractors and extended downtime.
The Unseen Threat: Pest Infestations and Health Code Violations
Grease buildup and standing water create ideal breeding conditions for pests that can establish colonies quickly. Once established, these infestations require professional pest control services and ongoing monitoring to prevent recurrence.
Health department violations compound the financial impact through mandatory re-inspections, potential temporary closure orders, and the documentation that remains part of your facility’s permanent record. These violations appear in public databases that competitors, customers, and corporate oversight teams regularly monitor.
Shifting the Conversation: Framing Maintenance as an Investment
The most effective approach for securing maintenance budget approval involves reframing the conversation from expense management to risk mitigation. Instead of asking ownership to spend money on a problem that hasn’t happened yet, position scheduled maintenance as insurance against catastrophic operational failure.
Business Impact: Proactive maintenance creates predictable operational expenses that protect against unpredictable emergency costs. This approach transforms budget planning from reactive crisis management to strategic operational control, giving management teams the visibility and control they need for accurate financial forecasting.
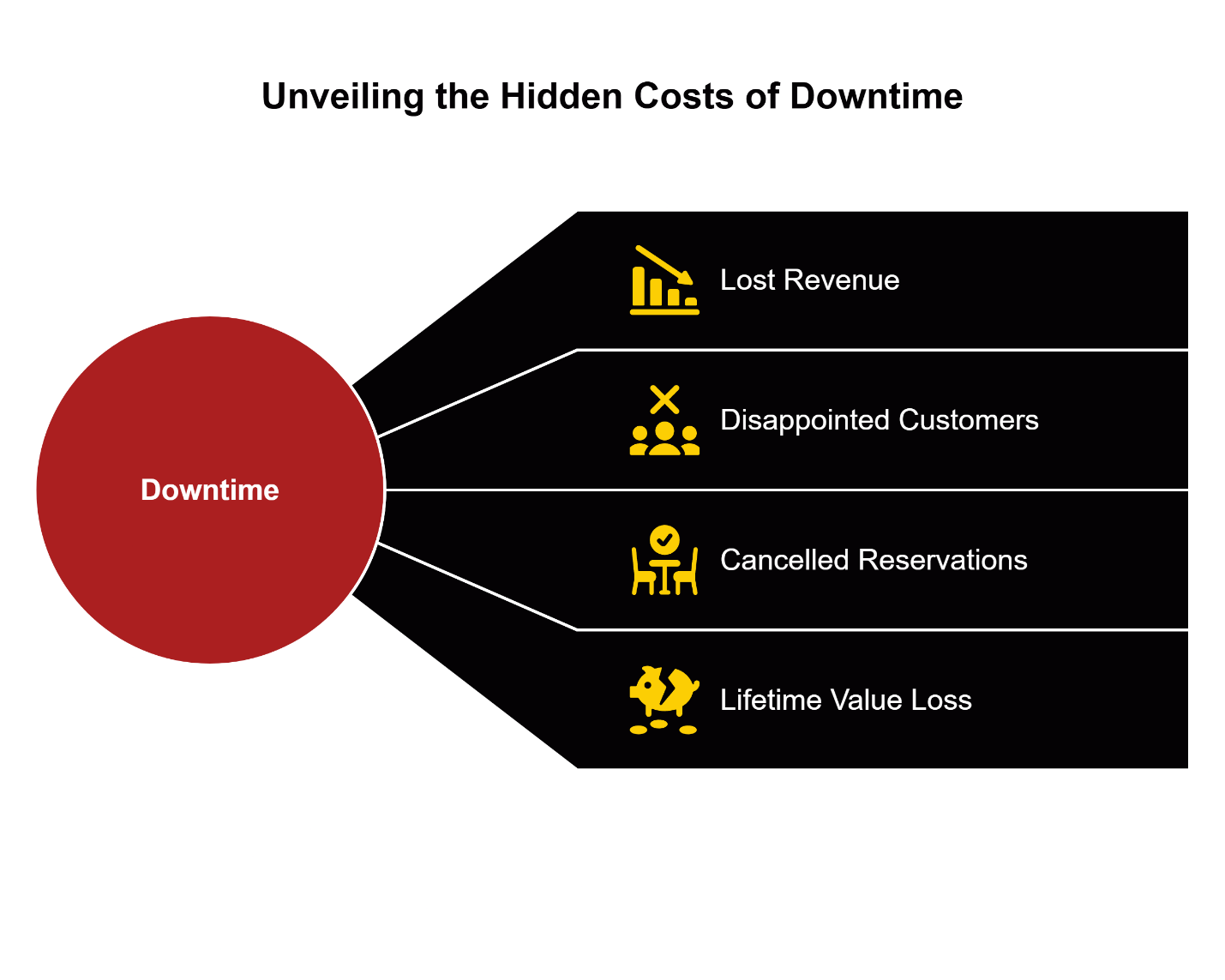
The 5 Hidden Costs of a Grease Trap Emergency
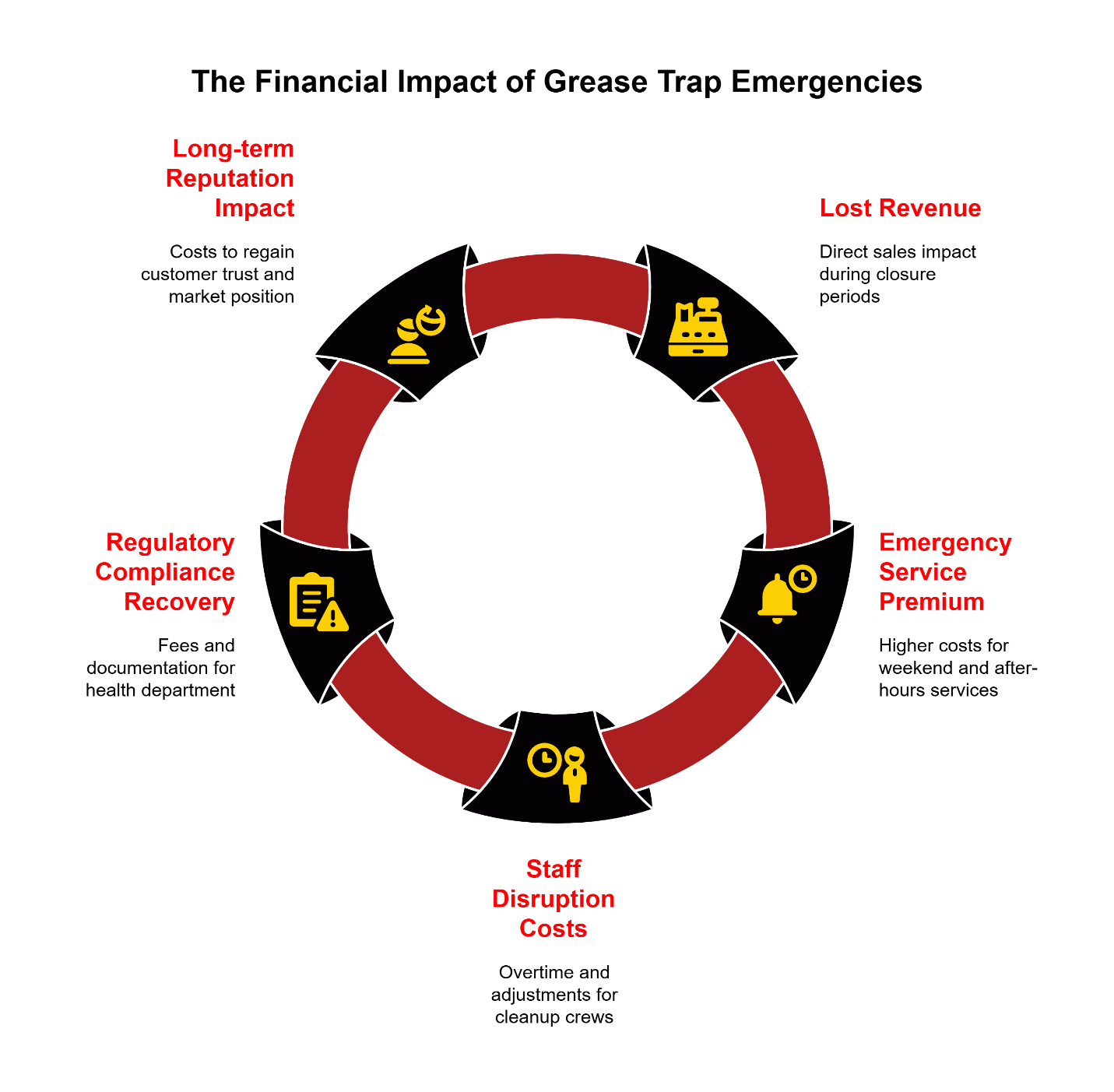
When presenting the business case for scheduled maintenance, focus on these specific cost categories that emergency situations generate:
- Lost Revenue During Shutdown – Direct sales impact during closure periods, including cancelled catering orders and drive-through diversions to competitors
- Emergency Service Premium – Weekend and after-hours service calls that cost substantially more than standard rates
- Staff Disruption Costs – Overtime for cleanup crews, compensation for sent-home employees, and temporary staffing adjustments
- Regulatory Compliance Recovery – Health department re-inspection fees, potential fine structures, and documentation management
- Long-term Reputation Impact – Customer acquisition costs to replace lost business, online reputation management, and competitive disadvantage during closure periods
This framework transforms abstract maintenance concepts into concrete financial projections that ownership teams can evaluate using standard business metrics.
“Scheduled maintenance isn’t a cost center; it’s an insurance policy against catastrophic operational failure and reputational damage.”
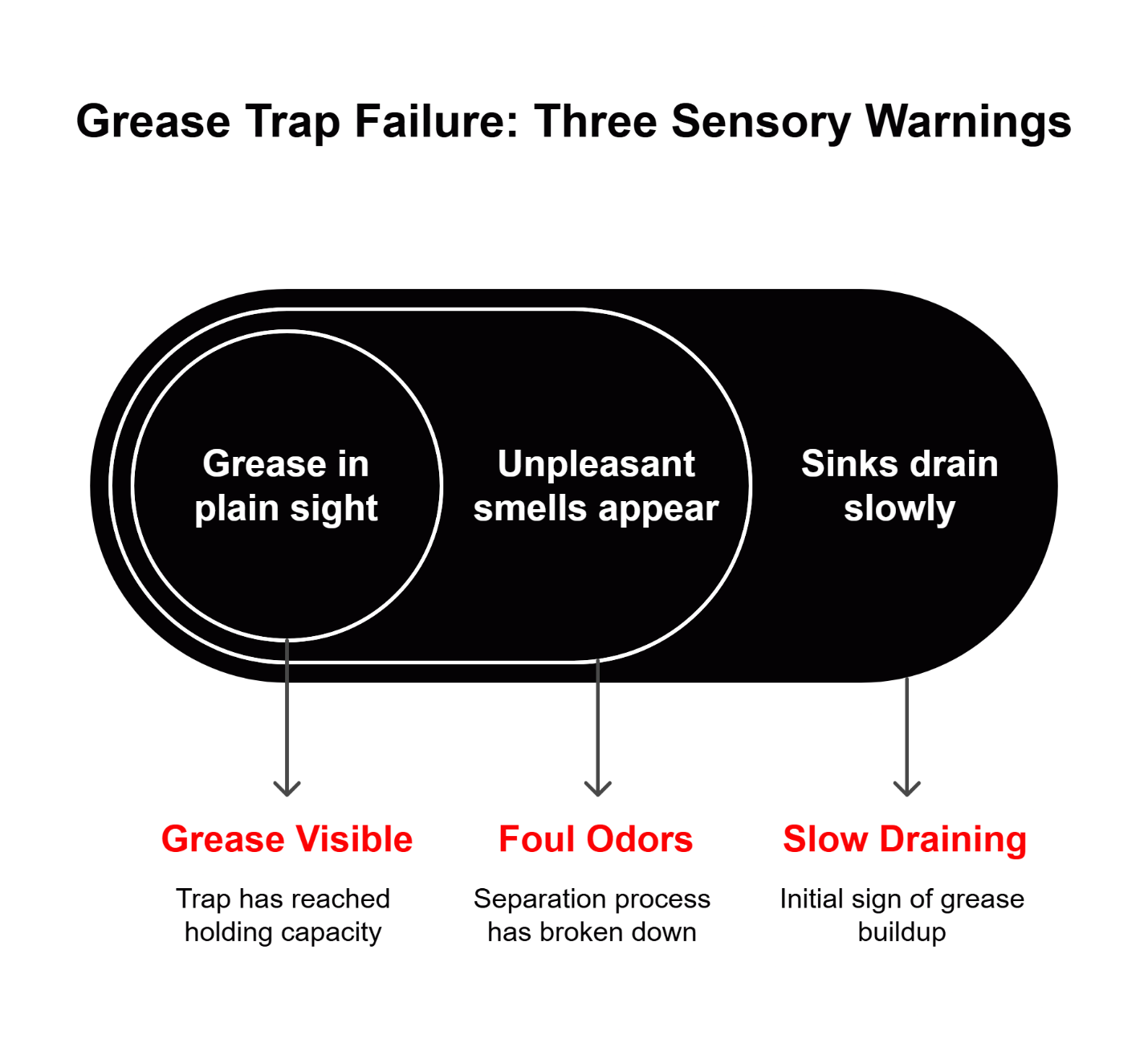
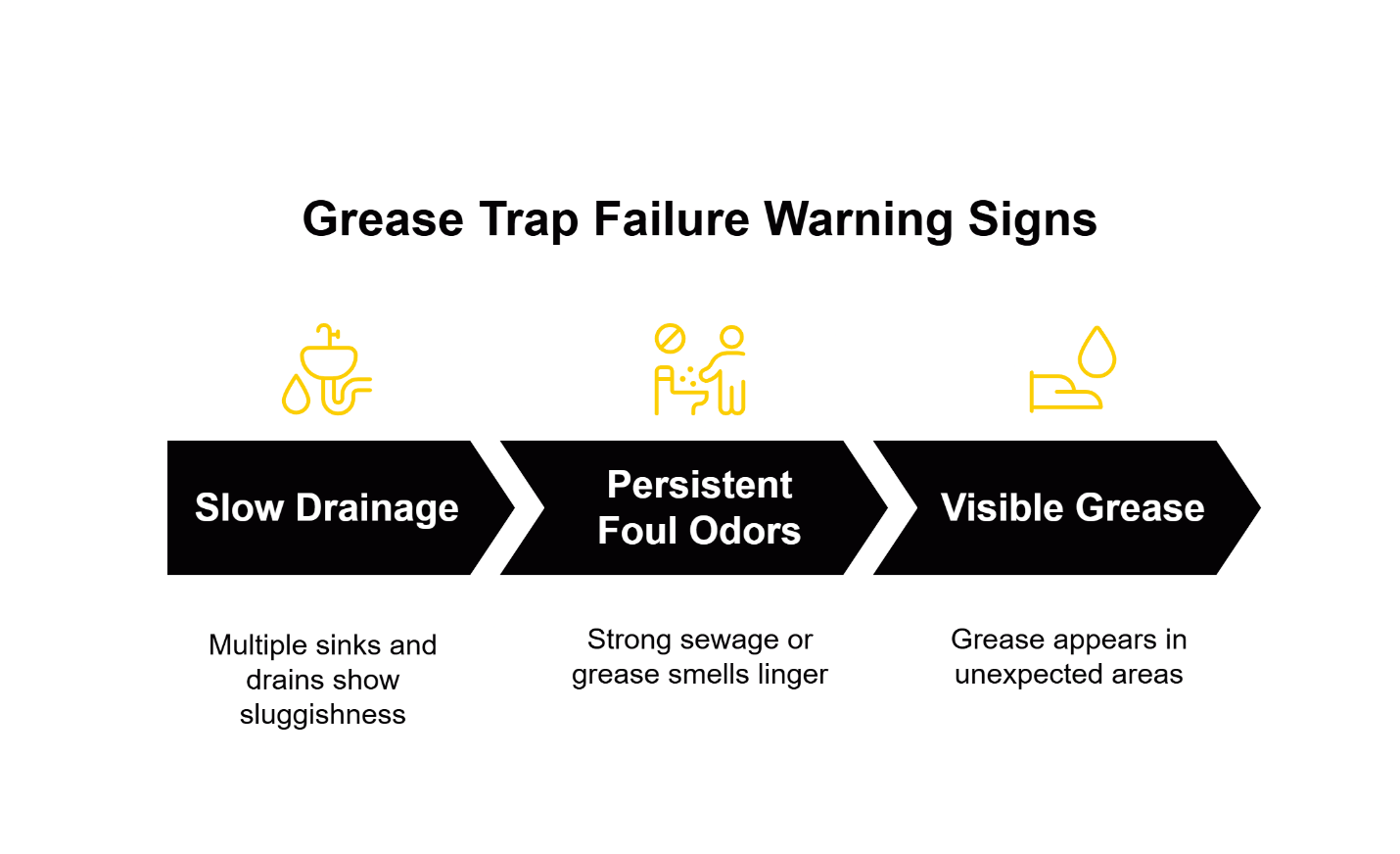
Technical Note: Many grease trap systems can provide warning signs of developing issues through drainage performance changes. However, these indicators require regular professional assessment to function effectively as predictive tools rather than reactive alarms.
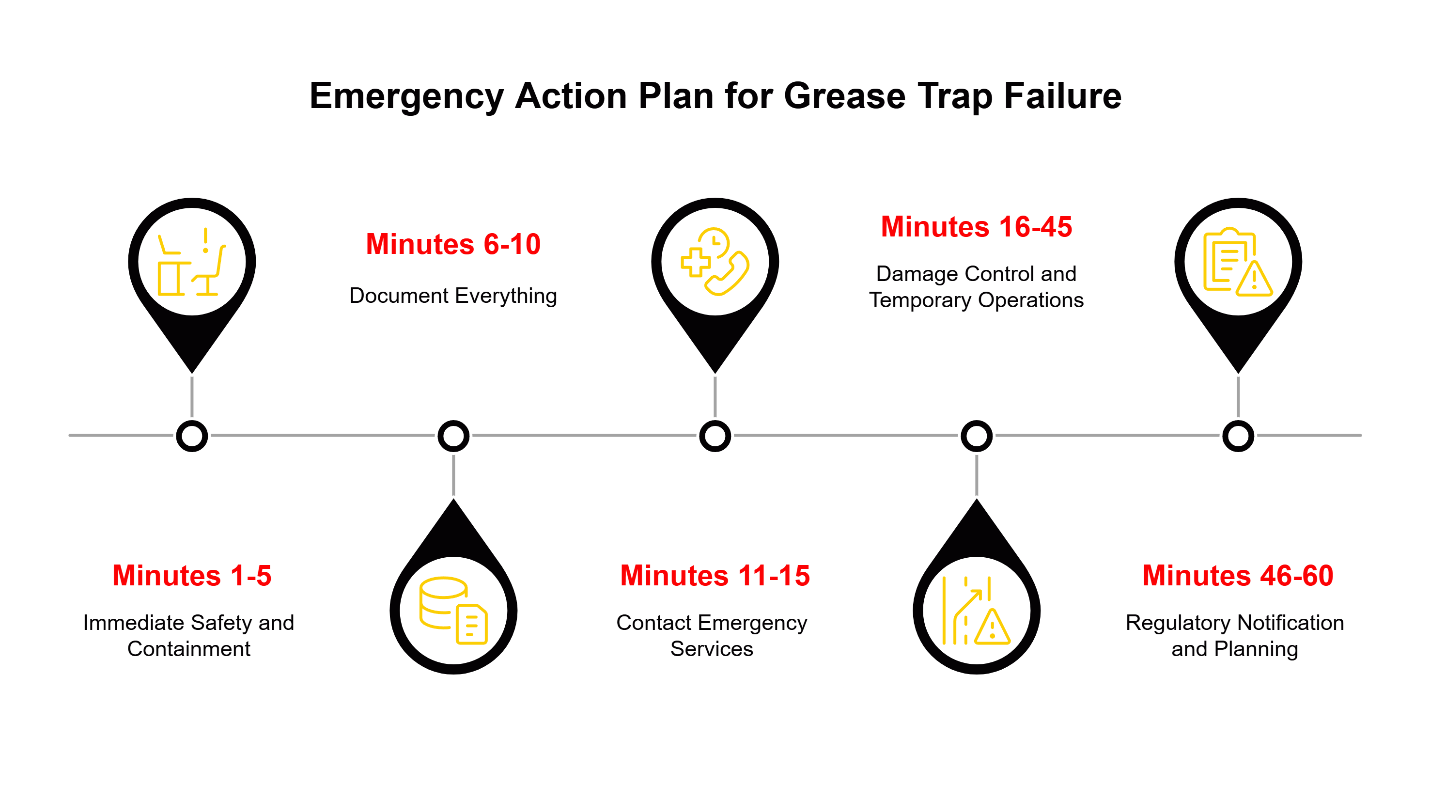
What If…? Planning for a Sudden Backup
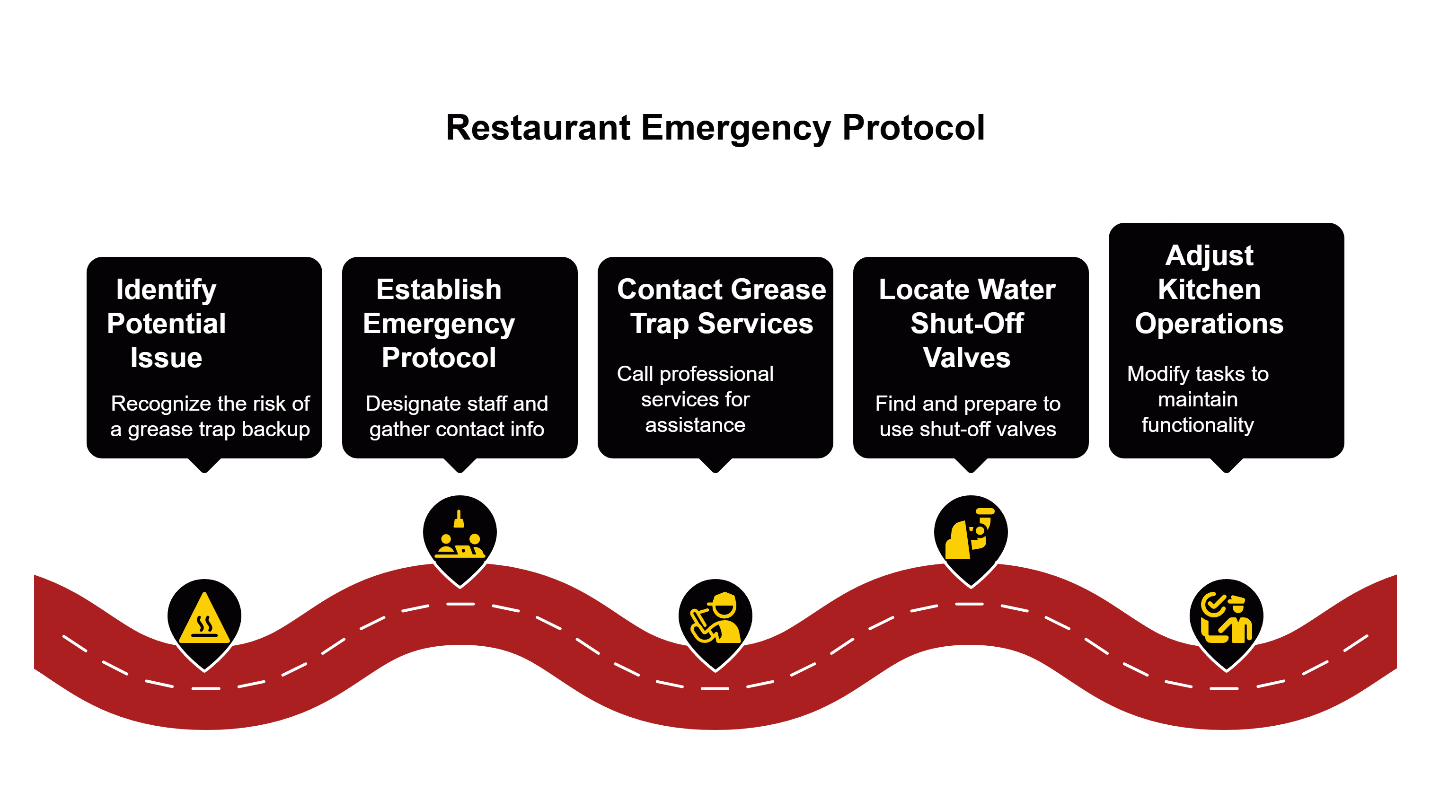
Even with scheduled maintenance, sudden backups can occur due to equipment failure, unusual waste volume, or upstream drainage issues. Having a clear response protocol reduces both downtime and associated costs when these situations arise.
First, establish relationships with emergency service providers before you need them. Research local vacuum truck services that offer after-hours response capabilities and understand your specific equipment configuration.
Second, train your management team to recognize early warning signs: slow drainage in prep sinks, unusual odors near floor drains, or visible grease accumulation in unexpected areas. Early intervention often prevents full system failure and the associated emergency response costs.
Myth: Scheduled grease trap cleaning is an unnecessary expense if we aren’t having problems.
Fact: Proactive cleaning is a low, predictable operational cost that prevents high, unpredictable emergency costs, protecting your budget and your business from sudden shutdowns.
A Question You Should Be Asking
What kind of long-term damage does a single, major backup cause to my restaurant’s plumbing system?
Beyond the immediate clog, hardened grease deposits can create ongoing drainage restrictions, leading to chronic issues that persist long after the initial emergency. A major backup can leave residual buildup that standard cleaning methods don’t fully remove, making your system more susceptible to future problems.
Professional maintenance prevents this cumulative damage by addressing grease accumulation before it hardens into permanent restrictions. The cost difference between preventing buildup and removing hardened deposits can be substantial, particularly when extensive remediation becomes necessary.
Day-to-Day Application: Implement a simple daily inspection routine where closing managers check drain flow rates in prep sinks and document any changes. This early warning system helps identify developing issues before they become operational emergencies, supporting both your maintenance schedule and your emergency response planning.
Conclusion: From Cost Center to Control Center
The argument for scheduled grease trap maintenance isn’t really about avoiding a city fine—it’s about maintaining operational control. When you position preventative maintenance as a strategic investment rather than a regulatory requirement, you’re demonstrating the kind of forward-thinking operational management that franchise ownership values.
Your role as operations manager involves balancing countless variables to maintain consistent service delivery. Grease trap maintenance might seem like a small piece of that puzzle, but its impact on overall operational stability is disproportionately large. The businesses that treat this maintenance as optional tend to learn this lesson the expensive way.
According to the Drane Ranger framework, the most critical factor is understanding that prevention costs are predictable while failure costs are not. The framework presented here gives you the tools to make a compelling business case based on risk mitigation and operational continuity rather than compliance requirements. More importantly, it positions you as a manager who understands the difference between managing costs and managing risks.
As you advance in your career toward regional management responsibilities, this understanding of operational interdependencies becomes even more valuable. Managing multiple locations requires the ability to identify systemic risks and implement preventative measures across diverse operational environments. The skills you develop in building these maintenance frameworks today become the foundation for managing larger, more complex operational challenges in the future.
The most successful restaurant operations managers don’t just respond to problems—they engineer systems that prevent problems from occurring. That’s the difference between managing a cost center and operating a control center.
Our Editorial Process
This guide was drafted with AI assistance and has been reviewed, fact-checked, and edited by the humans experts on our Insights Team to ensure accuracy and clarity.